SEO: How to Optimise your Website for Google Image Search

Bearing in mind that searching by
What Influences Image Ranking?
Despite the rapid development of Machine Learning, search engines are still having difficulties with the interpretation of what is shown within images.
5 HTML signals to help Google define whether the image matches the search query:
File Name
The file name should reflect the subject or narrative depicted in the image. It may be a word or phrase, but not just numbers or an incoherent set of characters. For the title of a photo of a product, you can use its brand, model and modification. For example,
Alt
The alt attribute contains text that the user sees instead of the image when it is not available for any reason (for example, displaying images is disabled in the browser or the page loads very slowly).
Also, the text written in alt is reflected in the Google image search. To get it right, follow these tips:
- Fill in alt for all images on the site (except adjunct images, such as lines or arrows);
- Write unique texts for each picture and include a key phrase that accurately describes the essence of the image;
- Don’t add an excessive number of keywords. Sticking to no more than 160 characters is recommended,
otherwise the search engine will not be able to accurately identify the essence of the image. - Don’t use words like “buy”, “order”, “price” unless they refer to the essence of the image (for example, when describing a price list or an order form).
Title
The title should be concise, so as to convey the essence of the image. This improves the user experience on your website, especially when there are many images on the page that require clarification (for example, different smartphone models).
- Use
hyphens, notunderscores (_) to connect separate words, as this is better for search engine recognition. - Do not write too long a title – 3-5 relevant words is enough.
Here is the correct syntax for inserting an image with regard to title and alt:
<img src = "image-name.webp" title = "the original title" alt = "here is the unique alt text" />
Textual environment
Searchers compare the received signals from the name of the image file with the alt attribute, i.e. the text of the links with the text surrounding the image.
Even if it is assumed that the image will be used without a textual environment (say, in the gallery), make a caption for it in the form of an explanatory phrase with a keyword.
External Anchor
Anchors are the text links to images, mainly added not on the page where the image is located but on other pages or even other domains.
- If you publish links to images somewhere, make the anchors descriptive. For example, when creating a link to a photo of a resort hotel, it’s better to use the anchor type “photo of the hotel N in London in summer 2018” than “here” or “in the photo”.
- If you implement all of these recommendations, your original pictures will be ranked not only in image searches but in regular search results via related keywords.
What is Sitemap for Images and What Does it Look Like?
In general, the sitemap is a file that contains a list of links to all the important pages on a site. That is, this document directs search engines to the main content to be indexed on the site.
In the case of images, it’s still difficult for search crawlers and bots to assign the images
XML Map for Images
Google supports extended syntax for images. Using the extended syntax in a sitemap provides the search engine with necessary information about the images on the site. It can also help Google to locate and index additional images which were not crawled and
Why Do You Need to Create an Image Site Map?
- To help Google discover and
recognise images in order to provide users with a better search experience
- To increase the traffic from Google SE without additional efforts, as you are creating interesting content for users by integrating the images in your content anyway.
- To achieve better rankings, the
fulfilment of special tags such as alt and image title for images is a positive factor.
Parameters to be Covered in the Image Sitemap
- Type of image file
- An image title
- The Alt text description for each image
- A geolocation (picture's GPS coordinates)
Should I Create a Separate Sitemap for Images or not?
You can create a separate sitemap for images or add the image-related URLs to an existing one. Just keep in mind the limitation from Google of 50K URLs to be placed within one sitemap and the restriction of the file size to 50MB. So, unless you’re managing a huge DB, you’re free to choose.
I would recommend creating a separate file “image-sitemap” as it makes the information look more structured when divided logically across several files.
Submit Image Sitemaps in Google Search Console
For the initial creation of the image
Note: if your site is less than 500 pages in total, the free version of Screaming Frog SEO Spider is enough. Otherwise, you’ll need a
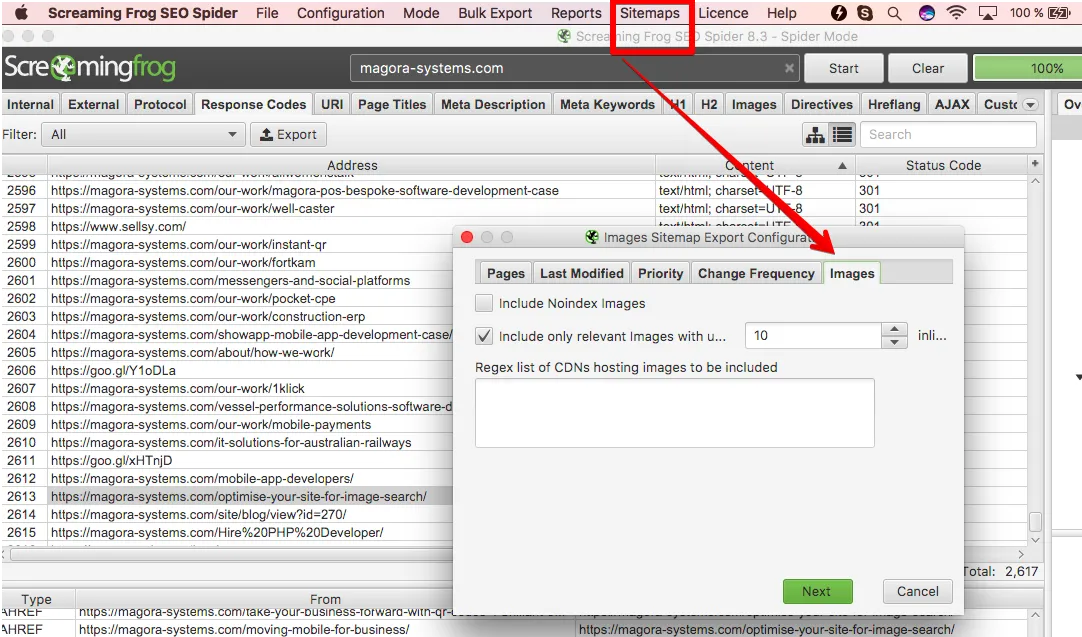
Note: You need to refresh the image sitemap any time you’re adding a new image to any page of your domain. Having a bespoke CMS demands working out additional functionality to let your images be integrated
The Image Sitemap plugin will generate a sitemap for your WordPress blog with all the image URLs that are attached to your blog posts and WordPress pages.” Here you’ll see the links to image and video sitemap generators by WP. “ https://wordpress.org/plugins/google-image-sitemap/
- And finally, you have to add the file to be crawled by Google. Add it to the Sitemaps in Google Search Console (ex.Google Webmaster Tool)
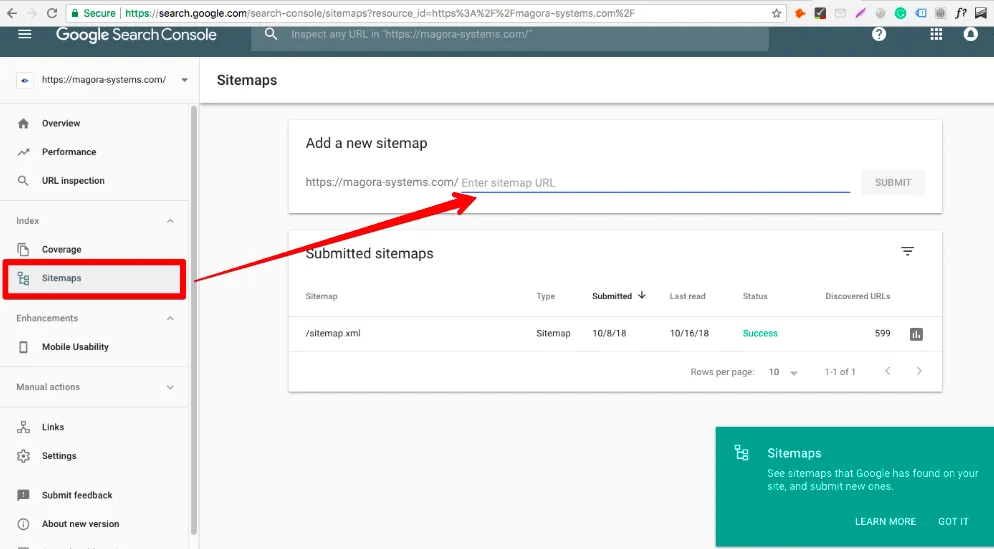
After submitting to Google, you may have to wait a few days for the search engine to start indexing uploaded images. You can view your image sitemap details in Google Search Console by clicking on the image sitemap.
One more way to submit your sitemap for Google SE is just to add it to the site, exactly the same way as you placed the regular sitemap.
- Note: don’t forget to add the reference about one more map to your robots.txt file.
Performing both actions will increase the chances of your images being crawled promptly.
If you need to remove images from the sitemap, read tips on how to do it here.
Keep in mind these important recommendations, provided by Google.
Opt out of image search inline linking
If you choose, you can prevent the full-sized image from appearing in Google's image search results page by opting out of inline linking in Google image search results.
To opt out of inline linking:
- When your image is requested, examine the HTTP referrer header in the request.
- If the request is coming from a Google domain, reply with HTTP 200 or 204 and no content.
Google will still crawl your page and see the
What to do if my pictures are not indexed for a long time:
- Check the indexing settings in robots.txt (it’s possible that search engines don’t have access to the uploads or
other folder where images are stored). Check the following page for an in-depth explanation regarding the robots txt file.; - Check if the page where the image is located is indexed (if not, check, again, robots.txt, for a ban on indexing in the robots meta tag or at the server level in the .htaccess file)
- Add the page where the image is located in the panel for webmasters like Google Search Console to speed up indexing.
8 Tips for Easy Image Optimisation
Follow these simple rules to receive additional free traffic from organic image searches.
Here are some quick tips to
- Use the correct format. Google can index image types in BMP, GIF,.webp,.webp and WebP formats, as well as SVG.
- Find an optimal solution between the size and quality of graphics. Pictures should be clear, visually appealing and consistent with the content of the page.
- Mind the size. Images must be created in the size in which they will be presented on the site.
- Give a brief corresponding description in the image file name.
- Store similar images in the same directory with an appropriate name.
- Build external anchor links to images. The text of the anchor must match the content of the image.
- Provide a broad and concisely descriptive image alt.
- Check your image-related sitemap with a Google testing tool (yes, you’ll need to log-in to your Google account in advance: https://www.google.com/webmasters/tools/sitemap-list)
One more thing: after you’ve finished with the image sitemap, the next step is to create the video sitemap. I’ve found some good instructions on how to create Video Sitemaps here.
The forward-thinking companies have websites especially rich in images and videos. If this sounds like you and the images on your site are not





